Multisystemic Adverse Reactions to Amlodipine Mimicking Vasculitis
Main Article Content
Abstract
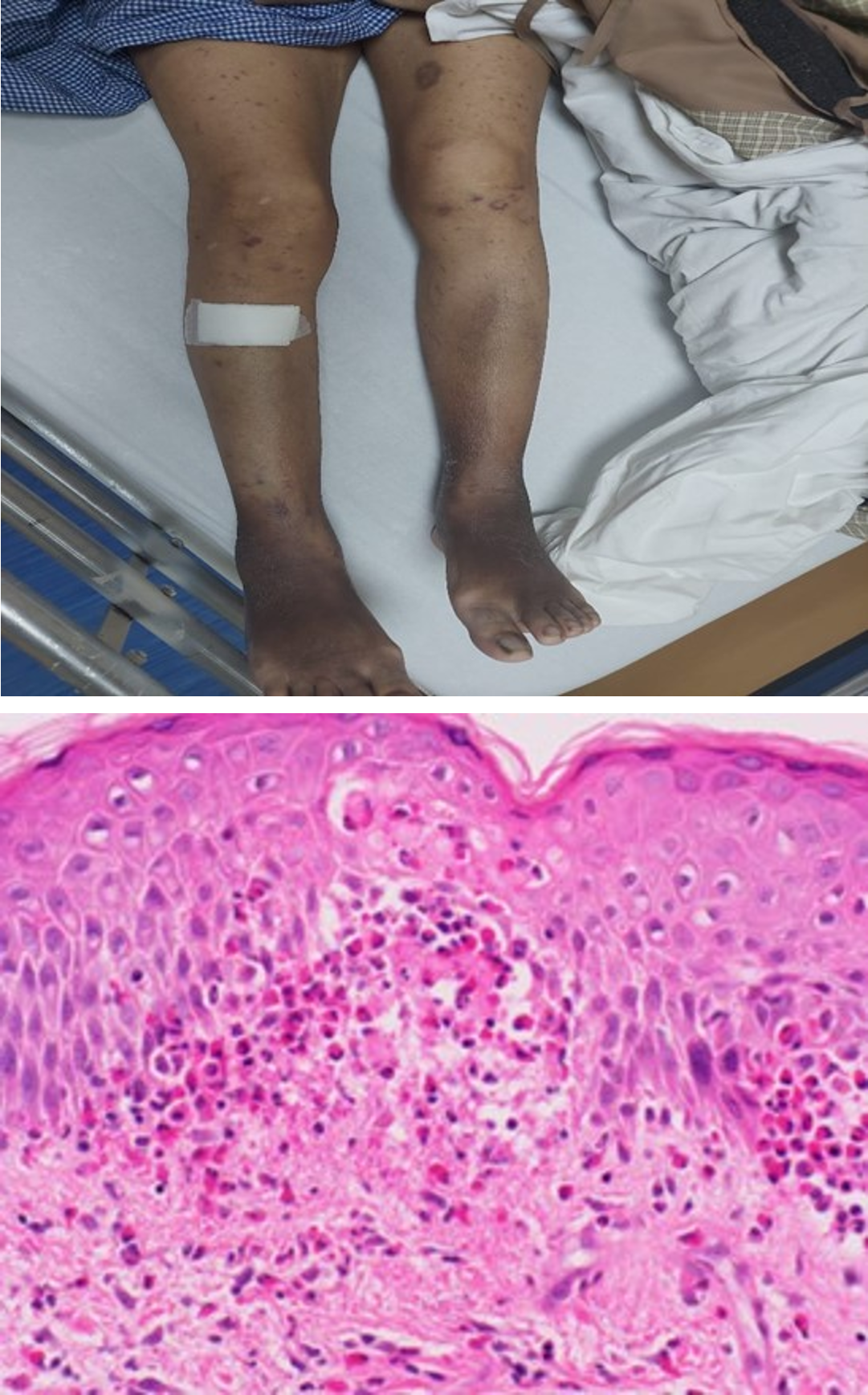
A 52-year-old lady, with hypothyroidism and hypertension for the last 2 months, presented with complaints of low-grade fever, gum hypertrophy, abdominal pain, palpable purpura, bilateral knee joint swelling, and bruising of both lower legs for the last 1 month. She had a significant fall in haemoglobin, a high Reticulocyte count, increased bilirubin level, and persistently high potassium with a positive Direct Coombs test. After the initial assessment, she was clinically diagnosed with an Adult-onset Henoch-Schonlein Purpura. She underwent skin biopsy, suggestive of Drug Rash- Amlodipine being implicated as the drug causing multisystemic manifestations. She was treated conservatively. Amlodipine was discontinued, and oral ketone and bilastine were started. She had a complete recovery.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the journal the right of first publication under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license, which allows others to share and adapt the work with proper attribution.
References
NHS. Amlodipine. National Health Service (NHS). 2022.
Audemard-Verger A, Pillebout E, Guillevin L, Thervet E, Terrier B. IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Shönlein purpura) in adults: Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Jul;14(7):579-85. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.02.003.
Bethesda. Adverse Drug Reaction Probability Scale (Naranjo) in Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Library of Medicine. 2012.
Amit Kumar Srivastava, Debabrata Kundu, Prasanta Bandyopadhyay, and Asit Kumar Pal. Management of amlodi-pine-induced gingival enlargement: Series of three cases. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2010 Oct;14(4):279-81. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.76931.
M Madi, SR Shetty, SG Babu, and S Achalli. Amlodipine-induced Gingival Hyperplasia – A Case Report and Review. West Indian Med J. 2015 Jun;64(3):279-82. doi: 10.7727/wimj.2014.089.
J. Devasahayam, U. Pillai, C. Uppaluri. Acute severe intestinal obstruction secondary to amlodipine toxicity. QJM: An In-ternational Journal of Medicine. Volume 105, Issue 5, May 2012, Pages 467–469.
Mayo Clinic. Amlodipine (Oral Route). 2022.
Denis Spelman and Rekha Pai Mangalore. Drug fever Topic 2738 Version 26.0. Uptodate. 2021.
MB Murthy and B Murthy. Amlodipine induced petechial rash. J Postgrad Med. 2011 Oct-Dec;57(4):341-2. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.90091.
Joseph T. DiPiro, Robert L. Talbert, Gary C. Yee, Gary R. Matzke, Barbara G. Wells, L. Michael Posey. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 10e, Drug-Induced Hematologic Disorders. 2017. TABLE e103-4 Drugs Associated with Hemolytic Anemia.
George Garratty. Drug-induced immune haemolytic anaemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009 (1): 73–79.
Grant SM, Goa KL, Fitton A, Sorkin EM. Ketotifen. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in asthma and allergic disorders. Drugs. 1990 Sep;40(3):412-48. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199040030-00006. Erratum in: Drugs 1991 Feb;41(2):192.
James Fernandez. 2024. Drug Hypersensitivity. MSD Manual Professional Edition. MSD Manual. 2024.