Vitamin D Intoxication Caused by a Manufacturing Error in a Prescribed Vitamin D3 Supplement, Successfully Managed with Low-Dose Zoledronic Acid
Main Article Content
Abstract
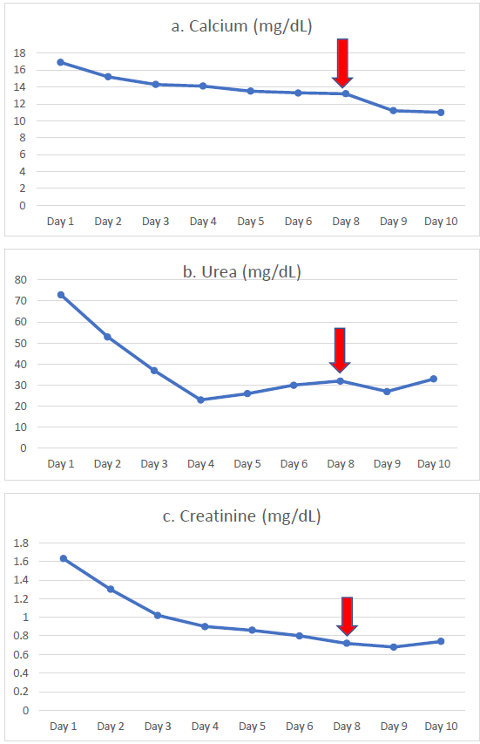
We describe a male toddler with a history of operated posterior urethral valves who developed vitamin D toxicity with hypercalcemia after he was prescribed orally 6,000 IU of cholecalciferol daily for two months for vitamin D deficiency. The disordered calcium metabolism was discovered during hospitalization in our hospital for a urinary tract infection, along with evidence of renal failure. Serum calcium on admission was 4.22 mmol/L, with an ionized calcium level of 2.26 mmol/L. The measured 25(OH)D level was extremely high (3,555 ng/mL), along with a low serum parathyroid hormone, suggestive of severe vitamin D overdose. Despite aggressive hydration, administration of corticosteroids, and a low calcium diet, he required the administration of a single dose of zoledronic acid for resolution of the hypercalcemia. It was later discovered that the patient received an oral solution of vitamin D3 that was recalled due to a higher content of vitamin D3 than stated on its label. Therapy with low-dose bisphosphonates is effective in cases of symptomatic hypercalcemia that does not respond to intravenous hydration, administration of corticosteroids, and elimination of oral calcium intake. Any child presenting with hypercalcemia and low parathyroid hormone should be investigated for the possibility of vitamin D toxicity.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their articles and grant the journal the right of first publication under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license, which allows others to share and adapt the work with proper attribution.
References
Holick MF. Vitamin D and bone health: What vitamin D can and cannot do. Adv Food Nutr Res 2024;109:43-66. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2024.04.002.
Wagner CL, Greer FR. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics 2008;122:1142-52. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-1862.
Munns CF, Shaw N, Kiely M, et al. Global consensus recommendations on prevention and management of nutritional rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:394-415. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2175.
Kaur P, Mishra SK, Mithal A. Vitamin D toxicity resulting from overzealous correction of vitamin D deficiency. Clin Endo-crinol (Oxf) 2015;83:327-31. doi: 10.1111/cen.12836.
Stokes VJ, Nielsen MF, Hannan FM, Thakker RV. Hypercalcemic disorders in children. J Bone Miner Res 2017;32:2157-70. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3296.
Marcinowska-Suchowierska E, Kupisz-Urbańska M, Lukasiewicz J, Płudowski P, Jones G. Vitamin D toxicity – A clinical perspective. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018;9:550. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00550.
Alonso N, Zelzer S, Eibinger G, Herrmann M. Vitamin D metabolites: Analytical challenges and clinical relevance. Calcif Tissue Int 2023;112:158-77. doi: 10.1007/s00223-022-00961-5.
National Osteoporosis Society. Vitamin D and bone health: A practical clinical guideline for management in children and young people. [Internet] Available at: https://nos.org.uk/media/2074/vitamin-d-and-bone-health-children.pdf (Accessed 2025 Jul 24).
Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011:1-1132.
The Medicines Optimization Team, Croydon CCG. Guidelines for the management of vitamin D deficiency in primary care. Children and young people – January 2019. 2021:1-18.
Galior K, Grebe S, Singh R. Development of vitamin D toxicity from overcorrection of vitamin D deficiency: A review of case reports. Nutrients 2018;10:953. doi: 10.3390/nu10080953.
Doyle KG, Blackstone MM, Barrett BC. Subacute gummy vitamin overdose as a rare manifestation of child neglect. Pediatr Emerg Care 2021;37:e479-82. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000001718.
Wani M, Wani I, Banday K, Ashraf M. The other side of vitamin D therapy: A case series of acute kidney injury due to mal-practice-related vitamin D intoxication. Clin Nephrol 2016;86:236-41. doi: 10.5414/CN108904.
Koul PA, Ahmad SH, Ahmad F, et al. Vitamin D toxicity in adults: A case series from an area with endemic hypovitaminosis D. Oman Med J 2011;26:201-4. doi: 10.5001/omj.2011.49.
Pandita KK, Razdan S, Kudyar RP, et al. "Excess gooD can be dangerous": A case series of iatrogenic symptomatic hypercal-cemia due to hypervitaminosis D. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 2012;9:118-20.
Buckle RM, Gamlen TR, Pullen IM. Vitamin D intoxication treated with porcine calcitonin. Br Med J 1972;3:205-207. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5820.205.
Mete E, Dilmen U, Energin M, Ozkan B, Güler I. Calcitonin therapy in vitamin D intoxication. J Trop Pediatr 1997;43:241-2. doi: 10.1093/tropej/43.4.241.
Song A, Chen Y, Chen R, Liu S, Kou L, Wang J, Nie M, Jiang Y, Li M, Xia W, Xing X, Wang O. The Efficacy and Safety of De-nosumab for Treating Hypercalcemia in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Retrospective Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Mar 3:dgaf107. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf107.
Barth K, Sedivy M, Lindner G, Schwarz C. Successful treatment with denosumab for two cases with hypercalcemia due to vitamin D intoxication and associated acute kidney injury. CEN Case Rep. 2022;11(1):141-5. doi: 10.1007/s13730-021-00643-5.
Tebben PJ, Singh RJ, Kumar R. Vitamin D-mediated hypercalcemia: Mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Endocr Rev 2016;37:521-47. doi: 10.1210/er.2016-1070.
Simm PJ, Biggin A, Zacharin MR, et al. Consensus guidelines on the use of bisphosphonate therapy in children and adoles-cents. J Paediatr Child Health 2018;54:223-33. doi: 10.1111/jpc.13768.
Kilci F, Jones JH, Çizmecioğlu-Jones FM. Successful management of severe hypercalcemia with zoledronic acid: A report of two pediatric cases. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 2024;16:224-8. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2022.2022-9.